
News







A study published today in Nature Microbiology holds promise for a new treatment method against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The star-shaped structures, are short chains of proteins called peptide polymers, and were created by a team from the Melbourne School of Engineering.

If you get pneumonia, or even an infected cut, your body is now a war zone. And as your immune system battles the invading bacteria, the outcome of that war may hinge on a microscopic arms race based not on missiles or bombs, but on an essential element: iron. Now, scientists from the University of Michigan Medical School say they have figured out how that race for iron actually increases the risk we face from one of our most dangerous microscopic foes, Klebsiella pneumoniae. They made the discovery in mice with pneumonia.

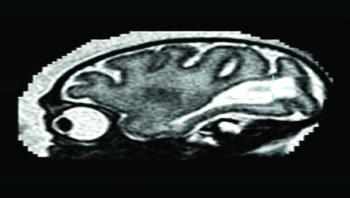
For the first time, abnormal brain development following a Zika infection during pregnancy has been documented experimentally in the offspring of a non-human primate. The researchers' observations of how Zika virus arrested fetal brain formation in a pigtail macaque could provide a model for testing therapeutic interventions.









Groundbreaking research from the University of Alberta has identified the structure of the infectious prion protein, the cause of mad cow disease, chronic wasting disease in deer and elk, and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans, which has long remained a mystery.









