
News





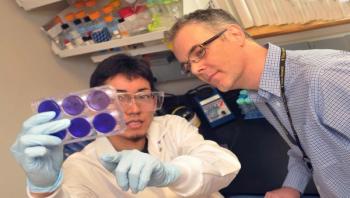
New research that focuses on the mechanism by which Ebola virus infects a cell and the discovery of a promising drug therapy candidate published Feb. 27 in the journal Science. Dr. Robert Davey, scientist and Ewing Halsell Scholar in the Department of Immunology and Virology at Texas Biomedical Research Institute announced today that a small molecule called Tetrandrine derived from an Asian herb has shown to be a potent small molecule inhibiting infection of human white blood cells in vitro or petri dish experiments and prevented Ebola virus disease in mice.



Sexual biology may be the key to uncovering why Anopheles mosquitoes are unique in their ability to transmit malaria to humans, according to researchers at Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health and University of Perugia, Italy. Through analysis of 16 Anopheles genomes, they found that these mosquitoes’ reproductive traits evolved along with their capacity to transmit the Plasmodium parasite that causes malaria. These findings may provide a new target for malaria control, particularly in regions hardest hit by the disease.

Up to 1 million people -- mainly pregnant woman and young children -- are killed each year by the Plasmodium falciparum parasite, which causes the most devastating form of human malaria. Now, researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have revealed the genetic trickery this deadly parasite deploys to escape attack by the human immune system.
The current global influenza situation is characterized by a number of trends that must be closely monitored. These include: an increase in the variety of animal influenza viruses co-circulating and exchanging genetic material, giving rise to novel strains; continuing cases of human H7N9 infections in China; and a recent spurt of human H5N1 cases in Egypt. Changes in the H3N2 seasonal influenza viruses, which have affected the protection conferred by the current vaccine, are also of particular concern.














Researchers explore individuals' confidence or reluctance to vaccinate their families and the associated effects on global health, in a collection published on Feb. 25 by the open-access journal, PLOS Currents: Outbreaks. The collection is accompanied by the editorial "Hesitancy, trust and individualism in vaccination decision-making" by Jonathan E. Suk et al. from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC).
