
News






The University of Georgia's Mark Ebell wasn't impressed with research on infectious mononucleosis when he wrote his first published review on it back in the 1990s. He still isn't--a subject he discusses in the April issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association.






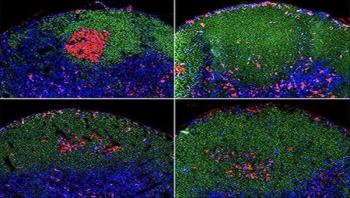
Follicular helper T cells (Tfh cells), a rare type of T cells, are indispensable for the maturation of antibody-producing B cells. They promote the proliferation of B cells that produce highly selective antibodies against invading pathogens while weeding out those that generate potentially harmful ones. In their latest study, researchers at La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology identified a key signal that drives the commitment of immature Tfh cells into fully functional Tfh cells and thus driving the step-by-step process that results in a precisely tailored and effective immune response.





When assigning blame for a number of outbreaks linked to contaminated and improperly processed duodenoscopes, a U.S. Senate report released in January pointed equally to hospitals, scope and equipment manufacturers and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for failing to act on known risks of infection. Duodenoscopes have been implicated in at least 250 patient infections with carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae (CRE) between 2012 and the spring of 2015.







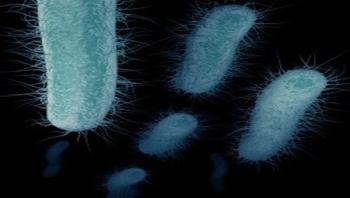

Exposure to pathogens early in life is beneficial to the education and development of the human immune system. Over the past few decades, the healthcare community has observed an intriguing phenomenon: diseases related to the immune system -- type 1 diabetes, and other autoimmune diseases, allergies, and the like -- have taken hold in countries that have thriving, modern economies, while barely making a mark in the developing world. One of the best-supported theories to explain this peculiar public health pattern has been dubbed the hygiene hypothesis. The theory is based on the premise that exposure to pathogens early in life is actually beneficial to the education and development of the human immune system.


