
News





The second meeting of the Emergency Committee (EC) convened by Margaret Chan, MD, the director-general of the World Health Organization (WHO) under the International Health Regulations (2005) (IHR 2005) regarding clusters of microcephaly cases and other neurological disorders in some areas affected by Zika virus was held by teleconference on March 8, 2016.














A new study of gut bacteria in premature infants reveals the vast scope of the problem of antibiotic resistance and gives new insight into the extreme vulnerability of these young patients, according to researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.


Many viral diseases tend to become chronic - including infections with the HI virus. In persons affected, the immune response is not sufficient to eliminate the virus permanently. Scientists at the University of Bonn have now identified an immune factor which is partially responsible for this. Their results give rise to hopes for new therapeutic approaches. The work, which included researchers from the University of Cologne and the Technical University of Munich, is being published in the journal Nature Immunology.




Almost every second woman suffers from a bladder infection at some point in her life. Also men are affected by cystitis, though less frequently. In eighty percent of the cases, it is caused by the intestinal bacterium E. coli. It travels along the urethra to the bladder where it triggers painful infections. In "Nature Communications" researchers from the University of Basel and the ETH Zurich explain how this bacterium attaches to the surface of the urinary tract via a protein with a sophisticated locking technique, which prevents it from being flushed out by the urine flow.
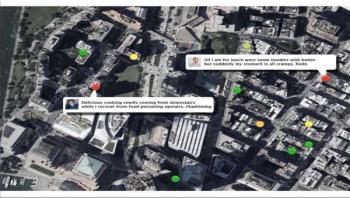
Foodborne illness afflicts 48 million people annually in the U.S. alone; 120,000 individuals are hospitalized annually, and 3,000 die from the illness. In fact, one out of every six Americans gets food poisoning each year. And many of these sufferers write about it on Twitter. Computer science researchers from the University of Rochester have developed an app for health departments that uses natural language processing and artificial intelligence to identify food poisoning-related tweets, connect them to restaurants using geotagging and identify likely hot spots.
