
News


Norovirus causes many people to become ill with vomiting and diarrhea each year. You can help protect yourself and others by washing your hands often and following simple tips to stay healthy.

The public's ability to understand the dangers posed by Zika virus may be jeopardized by advocacy groups linking the virus with culturally charged issues such as illegal immigration and global warming, the authors of a new study warn.
The gut of a child infected with rotavirus is like a battle ground. On one side, the virus invades the epithelial cells that form the lining of the small intestine. The virus replicates driving havoc in the intestinal environment, which causes severe diarrhea, vomiting, fever and abdominal pain. Dehydration usually follows and, unless the child is treated, death may be the end. On the other side of the battle, the body of the child fights back. Epithelial cells are the first responders to the viral attack and can produce antiviral compounds such as interferons (IFNs), in particular IFNs type I and III. What tips the balance in favor of the virus or the body's defenses has been hard to determine. Understanding how to give the body an upper hand would help save the lives of hundreds of thousands of children under 5 years of age, each year around the world.






Q: There has been a question from the staff here about leaving instruments overnight with an enzyme foam product on them. If we are here and a case comes in where the instruments were treated with the enzyme foam and we have time to wash them but will not be here long enough to run the load of instruments through the washer, is it best to leave them with the enzyme foam overnight or hand wash them and have ready to be put in the washer in the morning?
African-American adults are less likely than Caucasians to get an annual flu shot (39 percent versus 47 percent), and public health efforts to address this racial disparity have had little impact on increasing vaccination rates to date. A study led by professor Sandra Crouse Quinn in the University of Maryland School of Public Health is the first to explore racial factors and how they may influence vaccine attitudes and behaviors. The findings are published in the journal Vaccine
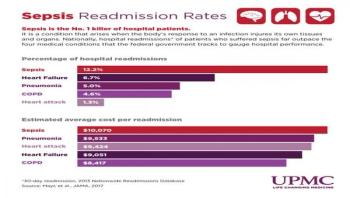
Sepsis accounts for considerably more hospital readmissions and associated costs than any of the four medical conditions tracked by the federal government to measure quality of care and guide pay-for-performance reimbursements, according to an analysis led by the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and VA Pittsburgh Healthcare System.

Over the last few years, a growing number of serious infections have been linked to bacteria forming in heater-cooler devices (HCDs) used in cardiac surgery operating rooms. In these cases, aerosolized bacteria, predominantly nontuberculous mycobacterium (NTM) from the HCDs, contaminated the operative field. Emerging evidence regarding the incidence and challenges of detecting the infections has triggered alarms at the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and regulatory agencies in Europe.











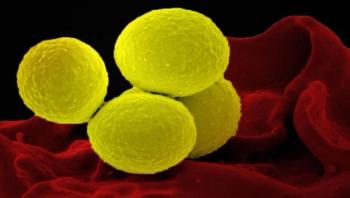
Scientists have discovered how a unique bacterial enzyme can blunt the body's key weapons in its fight against infection. Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and Newcastle University in the U.K. are investigating how infectious microbes can survive attacks by the body's immune system. By better understanding the bacteria's defenses, new strategies can be developed to cure infections that are currently resistant to treatments, the researchers said.


