
News



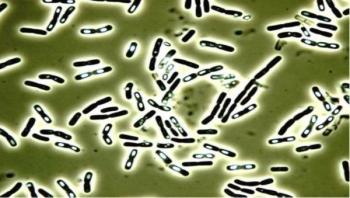
The Bacillus cereus bacteria is one of the potential causes of food poisoning. A recent study in Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry shows that this versatile pathogen produces 19 different variants of a poison that causes nausea and vomiting in human beings. This variety could explain why some cases are relatively benign and others can result in death.




Dr. Christina Lee, an Anglo-Saxon expert from the School of English has enlisted the help of microbiologists from University of Nottinham’s Centre for Biomolecular Sciences to recreate a 10th century potion for eye infections from Bald’s Leechbook an Old English leatherbound volume in the British Library, to see if it really works as an antibacterial remedy. The Leechbook is widely thought of as one of the earliest known medical textbooks and contains Anglo-Saxon medical advice and recipes for medicines, salves and treatments.


Cristiana Salvi, a risk communications specialist from WHO’s European regional office was deployed to Guinea at the end of April and into early May 2014 to provide social mobilization support to the Ebola response. Social mobilization involves working with communities to gain their acceptance of the need for early identification of people with illness, early treatment and identification and follow up of all people who have been in contact with people confirmed to have Ebola virus disease. Salvi was among the first from WHO offices other than headquarters and the African office to provide support to the field response, many others followed from the “wider WHO.” She traveled to Gueckedou where communities had begun to hide people who were sick, fearing treatment centers, believing rumours Ebola response teams were there for sinister purposes. This is what she found.

On a hot afternoon in November 2014, Benin’s minister of health, Dr. Dorothée Kinde Gazard and WHO country representative Dr. Youssouf Gamatié visited the Hôpital de Saint Jean de Dieu in Tanguiéta, in the country’s northwest. They were in a somber frame of mind. Four employees of the hospital had died from a severe febrile illness, some with signs of a viral hemorrhagic fever, over a period of two weeks – an event that for public health experts sounds the alarm for an outbreak of a dangerous infectious disease. Given the current Ebola virus disease outbreak in West Africa, one thing immediately came to mind – Benin could become the fourth.















Dr. Rob Fowler is a Canadian critical care physician from Toronto who was recruited by the World Health Organization in August 2013 to work with the Pandemic and Epidemic Diseases clinical team. When the Ebola outbreak was confirmed in late March 2014, Fowler was part of the first clinical response team to deploy to Guinea. In the months to follow, Fowler worked at an Ebola treatment center, focusing on treating dehydration, organ dysfunction and shock to drive down mortality rates.


Bioplastics made from protein sources such as albumin and whey have shown significant antibacterial properties, findings that could eventually lead to their use in plastics used in medical applications such as wound healing dressings, sutures, catheter tubes and drug delivery, according to a recent study by the University of Georgia College of Family and Consumer Sciences. The bioplastic materials could also be used for food packaging.

