
News










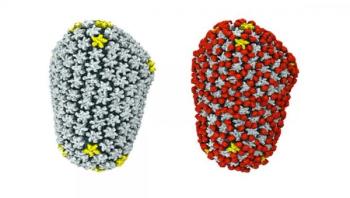
A new study offers the first atomic-scale view of an interaction between the HIV capsid - the protein coat that shepherds HIV into the nucleus of human cells - and a host protein known as cyclophilin A. This interaction is key to HIV infection, researchers say. A paper describing the research appears in the journal Nature Communications.












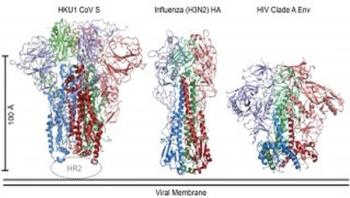
When the respiratory illness SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) emerged in 2003, it killed at least 775 people before it was contained. Nine years later, MERS (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome) began circulating in the human population-and has gone on to have a 36 percent case fatality rate.
State laws mandating influenza immunization for people who work in healthcare increase their vaccination rates, according to new research led by the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine.



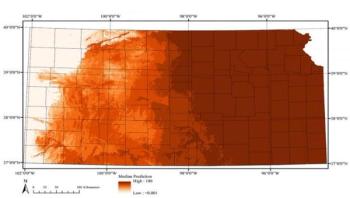
Climate change may have a new way of getting under your skin. Researchers in the College of Veterinary Medicine at Kansas State University have validated a model showing growth in Kansas for the habitat of the troublesome lone star tick. Previously thought only to live in the eastern third of the state, computational modeling and live specimens have revealed the existence of these ticks as far west as Colby, which is only 55 miles from the Colorado state line.
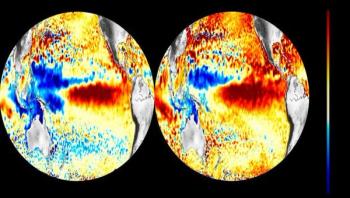
New research just published has highlighted how El Niño could be transporting and spreading waterborne diseases like cholera thousands of miles, across oceans, with significant impacts for public health. The study, published in the journal Nature Microbiology from a team of international researchers in the UK and U.S., explores how the arrival of new and devastating Vibrio diseases in Latin America has concurred in both time and space with significant El Niño events.