
News




Researchers from the University of Maryland, College Park, and Nanjing Medical University, China, have discovered a new way that white blood cells (neutrophils) defend our brains from infection -- they move the microbes from our brains' blood vessels or vasculature so they can be disposed elsewhere instead of just killing them at the site of infection. The final version of the report appears in the March 2016 issue of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology. "We hope our study opens a new field by using in vivo imaging to investigate how white blood cells interact with microbes in the brain, providing the scientific basis for targeting white blood cells as preventive and therapeutic interventions in brain infections," says Meiqing Shi, DVM, PhD, a researcher involved in the work from the Division of Immunology, Virginia-Maryland Regional College of Veterinary Medicine at the University of Maryland in College Park, Maryland.To make their discovery, the University of Maryland and Nanjing Medical University scientists used a form of microscopy, known as intravital microscopy, to visualize in mice the dynamic interactions of neutrophils with C. neoformans arrested in the brain microvasculature. This process enabled the observance of events in real time in living animals. They found that a therapeutic strategy aimed at enhancing the accumulation of neutrophils could help prevent cryptococcal meningoencephalitis. "New technologies, including the ability to microscopically visualize and watch the behavior of germs and immune cells in living tissues, are revolutionizing our understanding of infections and other diseases," says John Wherry, PhD, deputy Eeitor of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology. "These new studies that demonstrate the ability to neutrophils to move dangerous germs away from the brain makes us rethink the coordination in the immune response since these cells were previously thought to simply be soldiers killing germs wherever they found them."Reference: Mingshun Zhang, Donglei Sun, Gongguan Liu, Hui Wu, Hong Zhou, and Meiqing Shi. Real-time in vivo imaging reveals the ability of neutrophils to remove Cryptococcus neoformans directly from the brain vasculature. J. Leukoc. Biol. 99:467-473; doi:10.1189/jlb.4AB0715-281RSource: Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology
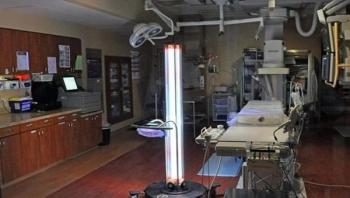
This case study explores how St. Mary's Health Care System in Athens, Ga. was the first healthcare institution in northeast Georgia to use UV light to treat high-utilization areas as an adjunct strategy to drive down their rates of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs).








St. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists have identified an enzyme that acts early in pneumococcal infections to promote bacterial survival and invasive disease by removing the bacteria's capsule. The research appears today in the scientific journal Nature Communications.



Directors of the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) have praised Brazil's research and actions on Zika virus and its possible consequences.






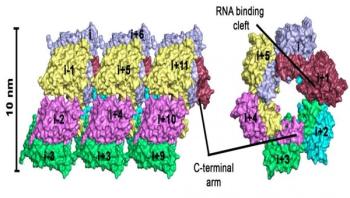
Bank voles are small rodents that are not dangerous by themselves, but their excreta can contain one of the dangerous hantaviruses. While bank voles are unaffected by the infection, hantaviruses can cause potentially fatal diseases in humans for which no treatments exist. In central and northern Europe, infection is accompanied by fever, headache, or even renal failure. The strain that occurs in East Asia -- the Hantaan virus -- is even more dangerous: up to 5 percent of infected patients die of hemorrhagic fever, renal failure, or severe respiratory disorders.
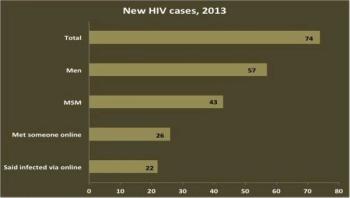
More than 60 percent of Rhode Island men who have sex with men (MSM) diagnosed with HIV in 2013 reported meeting sexual partners online in the preceding year, according to a study published today in the journal Public Health Reports.


Researchers from the University of Liverpool's Institute of Translational Medicine have conducted a study of Ebola survivors to describe the medical problems they continue to have after recovering from the acute disease. The results have been published in the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases.
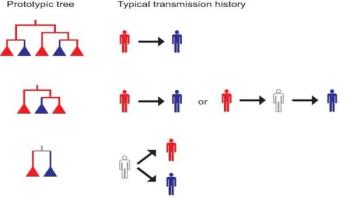
Scientists have a new tool for unraveling the mysteries of how diseases such as HIV move through a population, thanks to insights into phylogenetics, the creation of an organism's genetic tree and evolutionary relationships.

