News




The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) collaborated with public health officials in several states and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to investigate a multistate outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes infections (listeriosis). Listeria infection can cause a serious, life-threatening illness. This outbreak investigation is over; however, people could continue to get sick because recalled cheeses may still be in homes, restaurants or retail locations.







The Black Death has been infecting people centuries before the well-known 14th-century epidemic in Europe. In a new study reported in the journal Cell, researchers report that the bacterium Yersinia pestis, was infecting people as long as 5,000 years ago.
A team of international scientists led by Dr. Martin Olivier from the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC) uncovered an important mechanism behind Leishmania, a deadly parasitic disease transmitted by sandflies that affects over 12 million people worldwide, and with more than 1.3 million new cases reported every year. In a new study published today on the website Cell Reports, researchers described how key molecules known as exosomes, boost the process by which the Leishmania parasite infects humans and other mammals. These findings could lead to the development of new potential vaccine targets and diagnostic tools for Leishmania and other parasitic diseases.
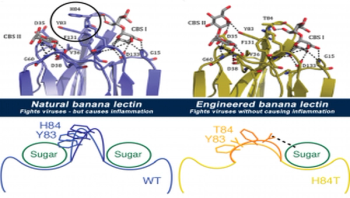
A banana a day may not keep the doctor away, but a substance originally found in bananas and carefully edited by scientists could someday fight off a wide range of viruses, new research suggests. And the process used to create the virus-fighting form may help scientists develop even more drugs, by harnessing the “sugar code” that our cells use to communicate. That code gets hijacked by viruses and other invaders.


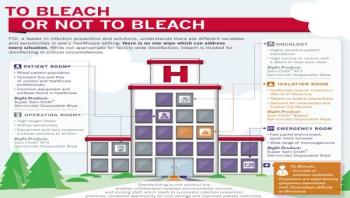
This report addresses the process by which sodium hypochlorite, the active ingredient in commercial bleach products, destroys disease-causing pathogens. It explains the science of how and why bleach is an effective disinfection agent, and presents information to address common misconceptions about bleach.

Scientists have identified a gene that could potentially open the door for the development of new treatments of the lethal disease sepsis.








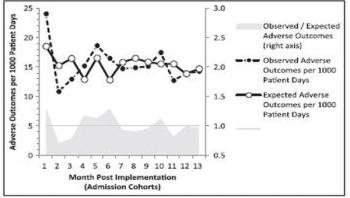
Sepsis is an inflammatory response to infection that's known to develop in hospital settings and can turn deadly when it's not discovered early on. In a new study, a hospital surveillance program focusing on reducing the risks of sepsis, known as the two-stage Clinical Decision Support (CDS) system, was found to reduce the risk of adverse outcomes, such as death and hospice discharge for sepsis patients, by 30 percent over the course of one year. This study is published today in the American Journal of Medical Quality.



During influenza season, which can start as early as October and end as late as May, tens of thousands of people visit physicians because of influenza-like illness (ILI). Given the concentrated volume of patients presenting with these symptoms and the similarity of ILI symptoms with those of other common respiratory infections, it is not surprising that these patients are generally treated empirically, without a formal diagnosis.