A new study by scientists at the Gladstone Institutes shows that infection sites could affect the immune system's response to a virus and the way the virus spreads through the body.

A new study by scientists at the Gladstone Institutes shows that infection sites could affect the immune system's response to a virus and the way the virus spreads through the body.

A review by Birgand, et al. (2018) provides an analysis of governance approaches within healthcare systems including: priority setting, performance monitoring and accountability for AMR prevention in three European countries: England, France and Germany.


A team of USC Viterbi School of Engineering researchers has created an algorithm that can help policymakers reduce the overall spread of disease.

Researchers have discovered crucial new processes that allow malaria parasites to escape red blood cells and infect other cells, offering potential new treatment targets.

Bacteria-killing viruses could be employed not just in healthcare, but also in the food industry, a study conducted at the University of Helsinki indicates.

Researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago will conduct a study to determine how the use of menstrual cups helps prevent vaginal infections and sexually transmitted infections.


With a new $15 million grant, scientists at the Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) are gearing up for an in-depth study of survivors of viral outbreaks.

A new blood test called the Tick-Borne Disease Serochip (TBD Serochip) promises to revolutionize the diagnosis of tickborne disease by offering a single test to identify and distinguish between Borrelia burgdorferi and seven other tickborne pathogens.
Flannery and Chung, et al. (2018) report that so far this season, influenza A(H3N2) viruses have predominated, but other influenza viruses are also circulating.
According to a new study, screening all adults for hepatitis C (HCV) is a cost-effective way to improve clinical outcomes of HCV and identify more infected people compared to current recommendations.
Researchers at La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology have identified a subset of T cells, whose frequency serves as early childhood immune signature that predicts the risk of developing asthma later on.

Anyone who has had chickenpox or the chickenpox vaccine is at risk for shingles.

Researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago have now identified a small drug molecule that can clear the HSV-1 infection in the cells of the cornea and works completely differently than the currently-available drugs, making it a promising potential option for patients who have developed resistance.

New diagnostic methods and treatments – including fecal transplantation – will help improve the care of patients with Clostridium difficile (C. diff.), a deadly bacterial infection that can occur after antibiotic use, according to updated guidelines released by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) and published in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases.

Queen’s University Belfast is playing a central role in an international consortium that has announced the development of a patch delivery system which will lower the chances of infection for those at very high risk of HIV.

Freedman, et al. (2018) reviewed documented coccidioidomycosis outbreaks from the period 1945–2015 to identify common features and prevention opportunities.

Material scientists at the University of Manchester, working in collaboration with universities in China, have created a 'durable and washable, concrete-like' composite material made from antibacterial copper nanoparticles.

A new study published in the Journal of Immunology offers new insights as to why healthy children are much more vulnerable to influenza.
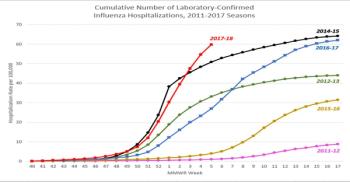
Budd, et al. (2018) report in MMWR that influenza activity in the United States began to increase in early November 2017 and rose sharply from December through Feb. 3, 2018; elevated influenza activity is expected to continue for several more weeks.


Fast, et al. (2018) designed a sterile processing education course, including mentoring, and aimed to evaluate the impact on participants’ personal knowledge, skills, and practices.

Infection prevention practices centered on hand hygiene protocols can save lives across all healthcare facilities, not just hospital settings.

The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) says it is alarmed by the proposed funding for critical programs needed to prevent, treat, and contain infectious diseases included in the President’s Budget Request.
In this retrospective study, the authors evaluated the association between Trypanosoma cruzi infection and strongyloidiasis in a cohort of Latin American migrants screened for both infections in the Hospital Clinic at Barcelona between January 2013 and April 2015.
Scientists at Imperial College London have become the first in the world to test how pathogens interact with artificial human organs.

In a paper published February 14 in Cell Host & Microbe, scientists provide a statistical model predicting which bacterial strains will engraft after FMT.