News















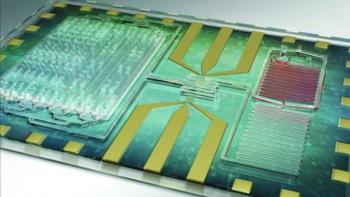
A team of researchers from the University of Illinois and Carle Foundation Hospital in Urbana, Illinois, completed a clinical study of the device, which is the first to provide rapid, point-of-care measurement of the immune system's response, without any need to process the blood.





The lack of clean water in many areas around the world is a persistent, major public health problem. One day, tiny robots could help address this issue by zooming around contaminated water and cleaning up disease-causing bacteria. Scientists report a new development toward this goal in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
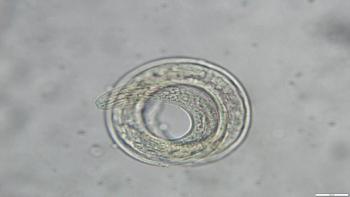
University of Florida researchers have found rat lungworm, a parasitic nematode that can cause meningitis in humans and animals, in five Florida counties. Rats and snails in Alachua, Leon, St. Johns, Orange and Hillsborough counties tested positive for the parasite, according to a study in PLoS ONE by researchers in the UF College of Veterinary Medicine and the Florida Museum of Natural History.