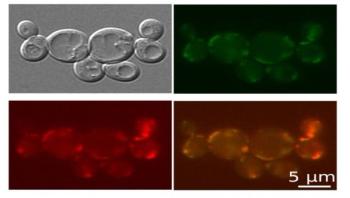
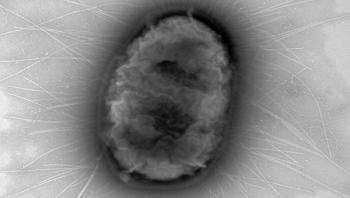
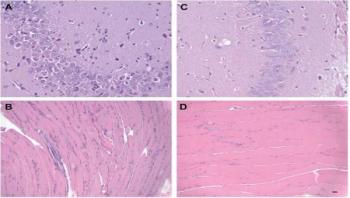
There are many reasons why bed bugs have made a comeback in recent decades, and their resistance to commonly used insecticides is one of the most widely accepted explanations. In a new paper published in the Journal of Economic Entomology, scientists from the University of Sydney and NSW Health Pathology describe how bed bugs are able to resist pyrethroid insecticides via metabolic detoxification, the process by which bed bugs break down insecticides.