
News




The world is poised to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030 – provided it can accelerate the pace of progress achieved globally over the past 15 years, according to a new World Health Organization (WHO) report.

In the fall of 1980, a 33-year-old immunologist named Michael Gottlieb began hearing about young homosexual men in the Los Angeles area who, inexplicably, were extremely ill. The men had a rare form of pneumonia – caused by the fungus Pneumocystis carinii (now called P. jirovecii) – which only strikes patients with severely weakened immune systems. The five men whose cases Gottlieb tracked did not know each other, and all but one had been in robust health until their physical conditions suddenly declined.

A program by Stony Brook Children’s Hospital that involves the use of trained community health workers on child immunization reveals that home intervention and education improves vaccine/immunization rates in at-risk children, including those living in poverty. Overall, the intervention improved the likelihood of up-to-date immunization status by more than 15 percent for children up to 2 years of age compared to those without the intervention. The study involved more than 300 pediatric patients and is published in the journal Vaccine.




Scientists at the Center for Infectious Disease Research recently uncovered a critical piece in the puzzle of how malaria parasites infect their host. The work, recently published in Science Magazine, reveals the details of how the malaria parasite invades its initial target organ, the liver. Without infection of the liver, the parasites cannot multiply or spread to the blood. Infection of the blood causes illness, spread of the disease, and, ultimately, death.








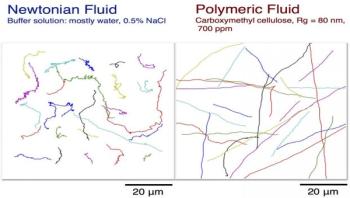
Swimming in a pool of syrup would be difficult for most people, but for bacteria like E. coli, it's easier than swimming in water. Scientists have known for decades that these cells move faster and farther in viscoelastic fluids, such as the saliva, mucus, and other bodily fluids they are likely to call home, but didn't understand why. Researchers from the School of Engineering and Applied Science and the School of Arts & Sciences have come together to find an answer. Their findings could inform disease models and treatments, or even help design microscopic swimming robots.





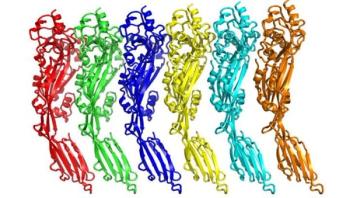
Scientists from the University of Leicester have for the first time created a detailed image of a toxin - called pneumolysin - associated with deadly infections such as bacterial pneumonia, meningitis and septicemia.


