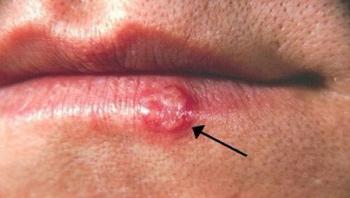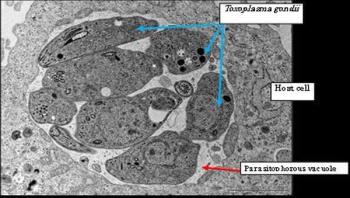
Toxoplasma gondii is a common parasite which causes the development of fatal encephalosis or pneumonia in immunodeficient patients under treatment of AIDS or cancer. Pregnant women who are infected may suffer a miscarriage or the newborn child may suffer from a congenital disease. Currently, a toxoplasma vaccine for humans is not available. Using experimental animals such as mice, basic research for developing an inactivated vaccine is underway.