News

A new Duke-NUS-led study has identified a super-potent antibody which requires a minute amount to neutralize the dengue virus. The study, published online on Feb. 20 in the journal Nature Communications, showed how a newly identified antibody 5J7, is highly effective in killing dengue virus whereby only 10-9 g of antibody is needed to stop the infection of dengue serotype 3 virus (DENV-3). This new finding gives hope for the development of effective dengue treatments.
Monika Ehling-Schulz's group from the Institute of Microbiology, together with Mathias Müller's group at the Institute of Animal Breeding and Genetics studied the influence of host organisms on bacterial metabolism. The researchers infected three different lineages of mice with the bacteria Listeria monocytogenes. The mouse strains showed significant differences in their response to the infection and in the severity of the clinical symptoms.




In a new study published in Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, researchers at the University of Alberta's faculty of medicine and dentistry have shown that a betaretrovirus which resembles a mouse mammary tumor virus infects patients with the rare liver disease, primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC).



The FDA wants to raise awareness among healthcare professionals, including those working in reprocessing units in healthcare facilities, that the complex design of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) endoscopes (also called duodenoscopes) may impede effective reprocessing. Reprocessing is a detailed, multistep process to clean and disinfect or sterilize reusable devices. Recent medical publications and adverse event reports link multidrug-resistant bacterial infections in patients who have undergone ERCP with reprocessed duodenoscopes, even when manufacturer reprocessing instructions are followed correctly. Meticulously cleaning duodenoscopes prior to high-level disinfection should reduce the risk of transmitting infection, but may not entirely eliminate it.



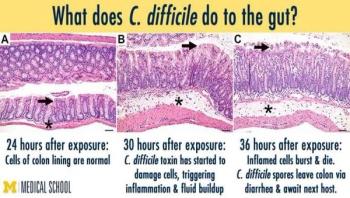
Sometimes, science means staying awake for two days straight. But losing sleep is a small sacrifice to make, if you want to learn more about tiny bacteria that sicken half a million Americans each year, kill more than 14,000 of them, and rack up $4.8 billion in healthcare costs. That's what drove a team of University of Michigan scientists to work around the clock to study Clostridium difficile, the bane of hospitals and nursing homes. Most patients develop it after taking antibiotics.

A clinical trial called HVTN 100 has been launched in South Africa to study an investigational HIV vaccine regimen for safety and the immune responses it generates in study participants. This experimental vaccine regimen is based on the one tested in the U.S. Military HIV Research Program-led RV144 clinical trial in Thailand-the first study to demonstrate that a vaccine can protect people from HIV infection. The HVTN 100 vaccine regimen was designed to provide greater protection than the RV144 regimen and has been adapted to the HIV subtype that predominates in southern Africa. The results of the HVTN 100 trial, expected in two years, will help determine whether or not this vaccine regimen will be tested for efficacy in a large future study in South Africa.
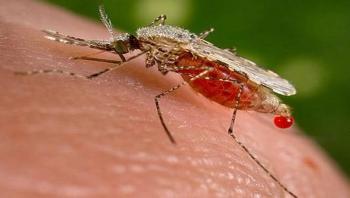
Researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine used algae as a mini-factory to produce a malaria parasite protein. The algae-produced protein, paired with an immune-boosting cocktail suitable for use in humans, generated antibodies in mice that nearly eliminated mosquito infection by the malaria parasite. The method, published Feb. 17 by Infection and Immunity, is the newest attempt to develop a vaccine that prevents transmission of the malaria parasite from host to mosquito.



Just how efficacious are the cleaning and disinfection interventions performed in healthcare institutions? And what standard are hospitals using to evaluate cleaning efforts? While it has been suggested that the food industry cleanliness standard (surface bioburden level of <2.5 cfu/cm²) be adopted in healthcare as an indication of relative cleanliness, there is still a lack of conclusive evidence that these levels of contamination relate to the prevention of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs).





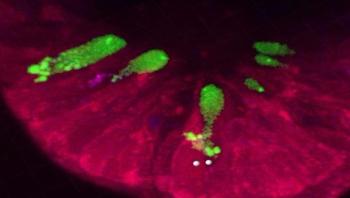
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder that affects one out of every 3,000 children in populations of Northern European descent. One of the key signs of cystic fibrosis is that mucus lining the lungs, pancreas and other organs is too sticky, which makes it difficult for the organs to work properly and, in the lungs, attracts bacteria and viruses resulting in chronic infections. Researchers at the University of Missouri recently found that cystic fibrosis mucus actually gets stuck inside some of the cells that create it, rather than simply becoming stuck on the outside linings of organs.
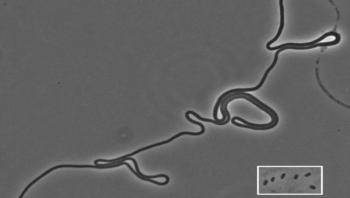
The typical Escherichia coli, the laboratory rat of microbiology, is a tiny 1-2 thousandths of a millimeter long. Now, by blocking cell division, two researchers at Concordia University in Montreal have grown E. coli that stretch three quarters of a millimeter. That's up to 750 times their normal length. The research has potential applications in nanoscale industry, and may lead to a better understanding of how pathogens work. The study was published ahead of print on Feb. 17 in the Journal of Bacteriology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.


In the northeastern United States, warmer spring temperatures are leading to shifts in the emergence of the blacklegged ticks that carry Lyme disease and other tickborne pathogens. At the same time, milder weather is allowing ticks to spread into new geographic regions. Findings were published this week in a special issue of the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B dedicated to climate change and vectorborne diseases.

The first publication out of a collaboration between Clarkson University and the Trudeau Institute aims to improve the fight against bacterial infections through immunoengineering. Chemical Communications has published a paper authored by researchers at Clarkson University and the Trudeau Institute, titled "Designed Supramolecular Filamentous Peptides: Balance of Nanostructure, Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Activity."