
Several previously healthy children were admitted for suspected hepatitis and tested positive for human adenovirus. Was there a connection?

Several previously healthy children were admitted for suspected hepatitis and tested positive for human adenovirus. Was there a connection?

Using COVID-19 precautions, and enhanced contact precautions and environmental hygiene, a COVID-19 isolation ward was able to contain an outbreak of CRAB.

Investigators search for increased speed, reliability, and durability in susceptibility testing for C difficile.
The Clostridioides difficile Health-related Quality-of-Life Questionnaire responses demonstrated patients handled the situation better with specific investigational treatments.

A recent study demonstrates a tool to help physicians better diagnose the cause of fevers in children.

Results unveiled at IDWeek 2021 disprove any misconceptions about pediatric COVID-19 cases lacking severity.

Pro: Health care professionals work around vulnerable patients, and in environments that might be contaminated by COVID-19. Con: Patients want to see their caregiver’s face.

The CDC’s Katryna Gouin, MPH: “…[I]deally tracking antibiotic use at the facility level should be automated using either electronic health records or long-term care pharmacy dispensing data because manual tracking of antibiotics is time intensive.”
Joshua Nosanchuk, MD, Programs Chairperson for ID Week: “What the infection preventionists are doing I think is a true blessing for our community. And not always as well recognized as it should be…. I just want to say thank you to all the people that are doing this work.”

The education of IPs has become a topic of interest since the onset of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The novel coronavirus highlighted that there perhaps are not enough IPs, and that’s especially true since their knowledge is being sought by schools, businesses and other non-healthcare settings.
Too many hospitals apparently do not use the CDC’s Hospital Toolkit for Adult Sepsis Surveillance, which may explain the number of healthcare-acquired infections that remain unreported.

When healthcare workers using the red box stepped into the patients’ rooms, there was “significantly increased non-compliance” with PPE and hand hygiene protocols compared to those healthcare workers who went into rooms without red boxes.

Investigators found that the mean healthcare cost for treating elderly influenza patients per patient per flu season ranged from $3,299 to $12,398 higher than the costs for treating patients with congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, coronary artery disease, and stage 5 renal disease.

Investigators found that a prompt on a disinfection tracking system led to an increase rate of the disinfection of computers on wheels at a veterans’ hospital in Texas.
Study: “There was no difference in the outcome in COVID-19 patients co-infected with influenza compared to non co-infected patients, however, a larger sample of cases will be needed for further assessment of these outcomes.”
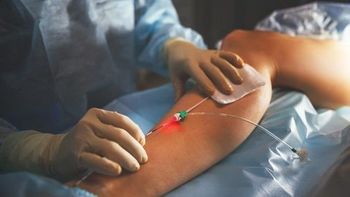
CAUTI rates were 83% higher and CLABSI rates were 65% higher in the COVID-19 units compared to the non-COVID-19 units.
There are 4 “moments” involved as a healthcare professional at a long-term care facility (LTCF) weighs whether to prescribe an antibiotic to a patient or resident.