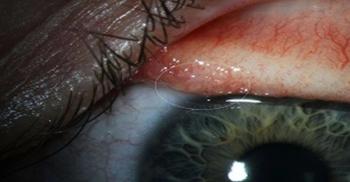
An August 2016 call to an infectious disease hotline OHSU runs for Northwest physicians ended up being one for the record books.

An August 2016 call to an infectious disease hotline OHSU runs for Northwest physicians ended up being one for the record books.

Opioid users have a significantly increased risk of infections severe enough to require treatment at the hospital, such as pneumonia and meningitis, as compared to people who don’t use opioids.
Closing a critical gap in knowledge, Harvard Medical School scientists have unraveled the immune cascade that fuels tissue damage and disease development in chlamydia infection.
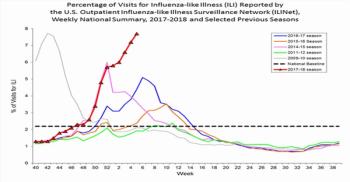
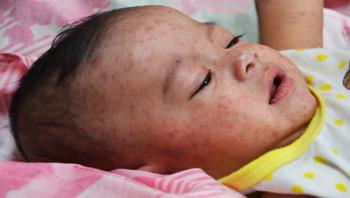
In the largest study to date on children in a low/middle income country, new research in Ghana finds that the timing of a measles vaccine in an overall vaccination schedule can have a profound impact on child survival rates beyond protecting against measles infection.
For the purposes of the R&D Blueprint, the World Health Organization (WHO) has developed a special tool for determining which diseases and pathogens to prioritize for research and development in public health emergency contexts.
A paper published in Clinical Infectious Diseases describes how infectious diseases physicians are uniquely positioned to lead programs guiding the use of antimicrobials.

The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is reporting that Pentax has issued an Urgent Medical Device Correction and Removal notification informing customers of its voluntary recall of all ED-3490TK duodenoscopes in order to replace the forceps elevator mechanism, O-ring seal and distal end cap, and to update the Operation Manual to recommend annual maintenance.


New research in Pediatric Dermatology reports several cases of shingles that developed at the original vaccination site in healthy children after they were immunized against chickenpox.

Continuous low doses of far ultraviolet C (far-UVC) light can kill airborne flu viruses without harming human tissues, according to a new study at the Center for Radiological Research at Columbia University Irving Medical Center (CUIMC).


The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) makes adherence to infection prevention and control recommendations easier than ever with their new mobile app, CDC DentalCheck.

A number of visitors to a New York City amusement park were found to have common respiratory viruses, according to a new study conducted by researchers at Columbia University’s Mailman School of Public Health.

The XXIII Olympic and Paralympic Winter Games will take place in PyeongChang, Republic of Korea Feb. 9-25, 2018 and Feb. 9-18, 2018, respectively.

Researchers from UConn Health are advancing the understanding of how the causative bacterial agent of Lyme disease, Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb), survives in ticks and mammals.
The human microbiome -- the trillions of tiny bacteria that live in and on our bodies -- is emerging as an increasingly important player in health and wellness. But, our co-existence with these organisms is complex, and scientists are learning that even minor changes in this relationship can lead to big problems with our health.
A new approach tested by researchers at the University of Iowa shows that de-identified data from a "smart thermometer" connected to a mobile phone app can track flu activity in real time at both population and individual levels and the data can be used to significantly improve flu forecasting.
The Veterans Health Administration, the largest integrated healthcare system in the United States, is leading efforts to prevent the spread of dangerous multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs), as detailed in a series of articles published in the February issue of Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
Ebola virus can infect the reproductive organs of male and female macaques, according to a study published in the American Journal of Pathology, suggesting that humans could be similarly infected


Despite efforts the elimination of yaws in a high-endemic community in Papua New Guinea (PNG) is yet to be achieved. The research identifies relapsing, untreated infections and the emergence of antibiotic resistance as contributing to ongoing yaws infection in the community. Researchers from Spain, PNG, the U.S., Australia, and international colleagues led the study.

A new blood test seems to perform as well as, if not better than, traditional blood cultures at detecting a type of fungal yeast infection that commonly strikes hospital patients, according to an analysis led by University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine (UPMC).


The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) says it is alarmed by the continuing resolution passed by the House of Representatives’ that would initiate a series of cuts to the Prevention and Public Health Fund in FY2021.
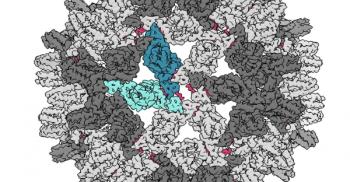
Indiana University researchers have made an important step forward in the design of drugs that fight the hepatitis B virus, which can cause liver failure and liver cancer.

Ants, like humans, deal with disease. To deal with the bacteria that cause some of these diseases, some ants produce their own antibiotics. A new comparative study identified some ant species that make use of powerful antimicrobial agents - but found that 40 percent of ant species tested didn't appear to produce antibiotics. The study has applications regarding the search for new antibiotics that can be used in humans.

As the fight against drug-resistant infections continues, University of Leeds scientists are looking back at previously discarded chemical compounds, to see if any could be developed for new antibiotics.

A new study indicates that the drug fosfomycin may be effective for treating multidrug-resistant bacterial infections.

A study published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry is the first to describe a signaling pathway that affects communication -- a process called quorum sensing -- between Streptococcus bacteria cells.