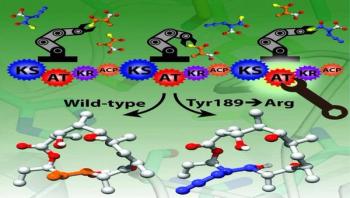
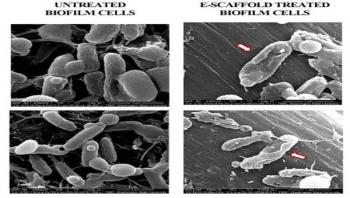
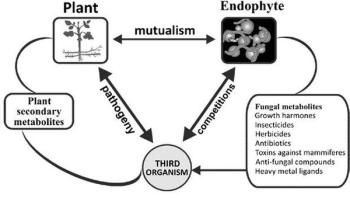
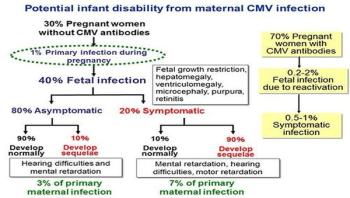
A new testing methodology based on metagenomics could accelerate the diagnosis of foodborne bacterial outbreaks, allowing public health officials to identify the microbial culprits in less than a day. The methodology could also identify co-infections with secondary microbes, determine the specific variant of the pathogen, and help alert health officials to the presence of new or unusual pathogens.