News



New research from North Carolina State University and the University of Michigan finds that bile acids which are altered by bacteria normally living in the large intestine inhibit the growth of Clostridium difficile, or C. diff. C. diff is a harmful bacterium that can cause painful and sometimes fatal infections. The work sheds light on the ways in which some commonly used antibiotics can promote C. diff infections by killing off the bile acid-altering microbes.









Research from the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Md., into better methods of predicting outbreaks of the mosquito-borne dengue virus was selected for presentation in September at the Eisenhower Executive Office Building - part of the White House complex. The APL team had developed new options for forecasting the spread of dengue fever, which affects up to an estimated 390 million people annually worldwide.



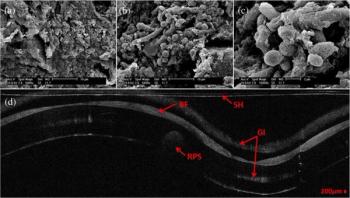
The ability to better detect and assess bacteria linked to a form of pneumonia prevalent in hospital intensive care units (ICUs) could soon become possible, according to research reported in the latest issue of the Journal of Biomedical Optics. The journal is published by SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics.