
News




In 2009, healthcare leaders and experts began to focus more intensely on the risks associated with the improper processing (cleaning, disinfection and/or sterilization) of reusable medical devices and equipment. Within the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) hospital system, the Memphis VA Medical Center (MVAMC) and other facilities initiated corrective actions to fine tune reprocessing policies, particularly those related to critical and semi-critical devices, to ensure compliance with manufacturers’ instructions for use. Since then, ensuring adequate device reprocessing has continued to be a concern for regulators, providers and medical device manufacturers. Ongoing discussions have led to direction such as an FDA draft guidance document for device manufacturers (FDA, 2011), and a report from the medical device reprocessing summit hosted jointly by AAMI and FDA (AAMI, 2011).





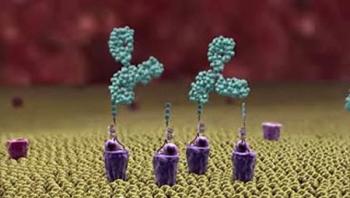
With the threat of multidrug-resistant bacterial pathogens growing, new ideas to treat infections are sorely needed. Researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences report preliminary success testing an entirely novel approach - tagging bacteria with a molecular “homing beacon” that attracts pre-existing antibodies to attack the pathogens. The study is published by the Journal of Molecular Medicine.

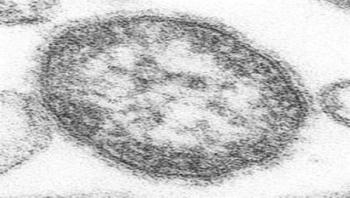
Gary W. Procop, MD, FCAP, a fellow of the College of American Pathologists, explains that measles is characterized by the three Cs: cough, coryza and conjunctivitis. This is followed by a maculopapular rash that usually develops 14 days after the child is exposed, spreading from head to trunk and then to the extremities. When the rash appears, the measles virus can spread.



Slips, trips, falls and sharps are widely recognized as potential occupational risks in the healthcare industry. However, there is another dangerous hazard that often goes unnoticed and underreported-splashes.





Johnson & Johnson (J&J) has donated the published proceedings from conferences on sterilization of medical products to the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI), which will make the material available online as a complimentary service to the sterilization community.


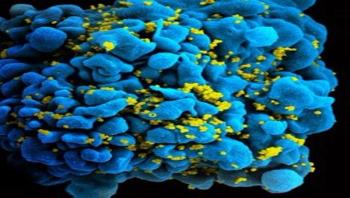
If the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a bit like a hermetically sealed tin can no one has yet been able to break open, the good news is that researchers at the CHUM Research Centre, affiliated with the University of Montreal, have identified a way to use a “can opener” to force the virus to open up and to expose its vulnerable parts, allowing the immune system cells to then kill the infected cells.



In Ebola-affected countries, like Sierra Leone, the lack of running water can make hand hygiene a challenge. Hand hygiene is so important in public health that May 5 every year is marked as Hand Hygiene Day. Dr. Komba Songu-Mbriwa is a doctor on the frontlines of the Ebola fight in Sierra Leone who also knows the challenges of the disease firsthand. He is an Ebola survivor. But today, he says his most important role extends beyond Ebola as a protector of other health workers. His specialty: teaching his colleagues how to protect themselves and other patients from the spread of all infectious diseases when patients are being cared for in health facilities.

