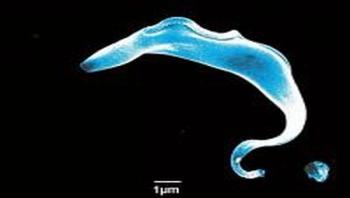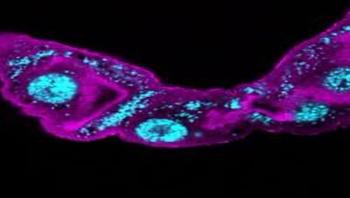
Wolbachia, a symbiont that resides naturally in up to 70 percent of all insect species, are probably the most prevalent infectious bacteria on Earth. In 2008 Luis Teixeira, now a principal investigator at the Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (IGC, Portugal), and other scientists have discovered that Wolbachia can protect their hosts against viral infections. Since then, several studies have been made to further investigate the interactions between Wolbachia and insects, aiming to build new strategies to use this bacterium in the control of diseases transmitted by mosquitoes, such as dengue. Now, Luis Teixeira's research team studied the genetic variability of Wolbachia strains and discovered that bacteria that give stronger protection against virus grow to higher concentrations and often shorten the host's lifespan. These results help to understand Wolbachia evolution in nature and open the way to the identification of the best strains to be used in the biocontrol of mosquito-spread diseases. This work was published in the latest issue of PLOS Genetics.