
News


ICT invited manufacturers of hand hygiene products to provide instruction on best practices relating to the evaluation of products as well as how to introduce and integrate them into the healthcare environment.


A National Institutes of Health-funded study led by a team at the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University has shown that an influenza vaccine can produce robust immune responses and be administered safely with an experimental patch of dissolving microneedles. The method is an alternative to needle-and-syringe immunization; with further development, it could eliminate the discomfort of an injection as well as the inconvenience and expense of visiting a flu clinic.



Israel is subjected to sand and dust storms from several directions: northeast from the Sahara, northwest from Saudi Arabia and southwest from the desert regions of Syria. The airborne dust carried in these storms affects the health of people and ecosystems alike. New research at the Weizmann Institute of Science suggests that part of the effect might not be in the particles of dust but rather in bacteria that cling to them, traveling many kilometers in the air with the storms.
Researchers from the University of Zaragoza (Spain) have analyzed drinking water and detected oocysts of Cryptosporidium and cysts of Giardia, two protozoa that cause outbreaks of diarrhea in humans. The levels detected are very low and do not represent a health risk; however, according to the study, the ubiquity of these parasites and the inefficiency of conventional water treatment in reducing them may present a public health issue.

St. Jude Children's Research Hospital immunologists have discovered how immune cells called T cells become "exhausted" -- unable to do their jobs of attacking invaders such as cancer cells or viruses. The finding is important because patients treated with immunotherapies against cancers are often non-responsive or experience a relapse of their disease, and it has been suggested that these challenges may be due to T cell exhaustion. In preclinical model systems studying viral infections or tumors, the researchers found that a chemotherapy drug already in use can reverse that exhaustion.
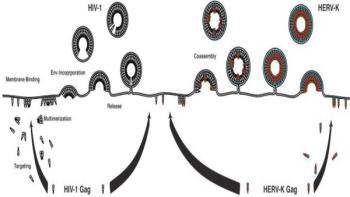
Throughout our evolution, viruses have continually infected humans just as they do today. Some early viruses became integrated into our genome and are now known as human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs). Over millions of years, they became inert due to mutations or major deletions in their genetic code. Today, one of the most studied HERV families is the HERV-K family, which has been active since the evolutionary split of humans and chimpanzees with some members perhaps actively infecting humans within the past couple hundred thousand years.

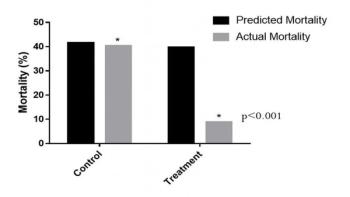
Sepsis presents a major challenge for healthcare providers, especially in low-income countries where the mortality rate can exceed 60 percent. Even in advanced medical settings, sepsis is still very dangerous and accounts for over 400,000 deaths annually in the U.S. alone. While new drugs are in development, a group of researchers has determined that a combination of intravenous vitamin C, corticosteroids (a steroid), and thiamine (vitamin B) may be effective in preventing progressive organ dysfunction and reducing the number of deaths from severe sepsis and septic shock. Their findings are published in the June issue of CHEST.




A pair of scientists at the University of Texas at El Paso is one step closer to developing the first ever clinical Chagas disease vaccine. Researchers Rosa Maldonado, PhD, and Igor Almeida, PhD, both faculty in the Department of Biological Sciences, recently were granted a patent for “Mucin-Associated Surface Protein As Vaccine Against Chagas Disease.”

The recent measles outbreak in Minnesota -- by June, new cases of the disease in that state surpassed nationwide totals for all of 2016 -- has been a sobering reminder of how highly concentrated populations of vaccination skeptics can elevate an entire community's risk of infection.




For decades, HIV has successfully evaded all efforts to create an effective vaccine but researchers at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) and the La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology (LJI) are steadily inching closer. Their latest study, published in the current issue of Immunity, demonstrates that optimizing the mode and timing of vaccine delivery is crucial to inducing a protective immune response in a preclinical model.
Previous research has shown that pairing antibiotics can be more effective than using single drugs, but finding these perfect matches has proven elusive. Researchers at University of Utah Health have developed a rapid screening method to identify beneficial pairs of existing FDA-approved drugs to combat multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacterial infections. The results are published online in PLoS Biology.
The use of topical antibiotics can dramatically alter communities of bacteria that live on the skin, while the use of antiseptics has a much smaller, less durable impact. The study, conducted in mice in the laboratory of Elizabeth Grice, PhD, an assistant professor of dermatology in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, is the first to show the long-term effects of antimicrobial drugs on the skin microbiome. Researchers published their findings today in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.





Patients with obesity have a higher risk of infection within 30 days after receiving heart bypass surgery, according to a series of studies conducted by University of Alberta researchers at the Faculty of Rehabilitation Medicine.