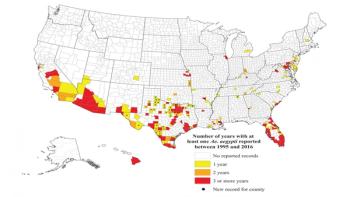
As concerns over Zika virus have grown since 2015, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has turned to local public health professionals to compile data on distribution of the two primary mosquito species capable of transmitting the virus, Aedes aegypti (the primary vector for Zika) and Aedes albopictus. Their findings highlight both the potential widespread presence of the mosquitoes as well as gaps in local surveillance capabilities crucial to understanding the threat of Zika and other mosquito-borne diseases such as dengue and chikungunya. Through a county-level survey of vector-control professionals, entomologists, and state and local health departments, conducted initially in 2015 and again in 2016, CDC researchers developed what they call "our best knowledge regarding the current distribution of Ae. aegypti and Ae. albopictus in the United States." Reported in the Entomological Society of America's Journal of Medical Entomology, the historical county-level records compiled by the CDC show Ae. aegypti reported in 220 counties in 28 states and the District of Columbia between 1995 and 2016 and Ae. albopictus reported in 1,368 counties in 40 states and DC during that time.