News





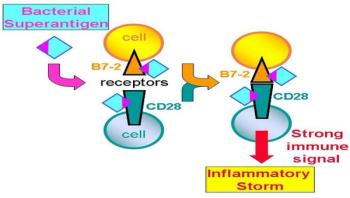
Staphylococcal and streptococcal infections affect millions of individuals each year. They are a leading cause of sepsis and account for many cases of pneumonia and post-surgical infections. Despite the urgency of this situation, the antibiotic development pipeline is dwindling and multi-drug resistance is rampant, rendering the classical one-bug, one-drug approach obsolete.





Simon Fraser University researcher Lisa Craig is part of an international team that has uncovered new details about a microbe that invades the brain, sometimes with fatal results. The information is a critical piece of the meningitis puzzle, and could lead to new ways of treating meningococcal infection. The research was published today in the journal Nature Communications.

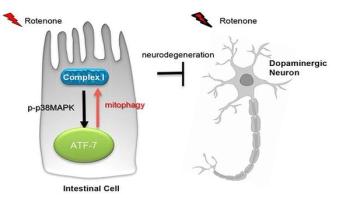
Researchers at the University of Iowa have found that the gut may be key to preventing Parkinson's disease. Cells located in the intestine spark an immune response that protects nerve cells, or neurons, against damage connected with Parkinson's disease. Acting like detectives, the immune intestinal cells identify damaged machinery within neurons and discard the defective parts. That action ultimately preserves neurons whose impairment or death is known to cause Parkinson's.


A new clinical study published in the American Journal of Infection Control confirms copper’s ability to continuously kill harmful bacteria in hospital settings. Grinnell College associate professor of biology Shannon Hinsa-Leasure, PhD, and her team conducted research over 18 months at Grinnell College and Grinnell Regional Medical Center (GRMC) in Iowa with more than 1,500 samples. The research found significantly fewer bacteria on copper alloy products such as grab bars, toilet flush valves, IV poles, switches, keyboards, sinks and dispensers than on traditional hospital room surfaces. In this case, products used in the study were made from CuVerro® copper alloys, one of several EPA-registered brands of antimicrobial copper materials.






A Biosecurity Research Institute study has found important results in the fight against Zika virus: Culex mosquitoes do not appear to transmit Zika virus. Researchers at Kansas State University's Biosecurity Research Institute studied Culex species mosquitoes from across the country, including Vero Beach in Florida, which is near Miami-Dade County where mosquitoes are spreading Zika virus.