
News










Since armed unrest erupted more than four years ago in Syria, resulting in huge movements of the population inside the country and spilling into neighboring countries, WHO has taken a lead role – one that continues in the face of crippling funding shortfalls - to support the displaced.


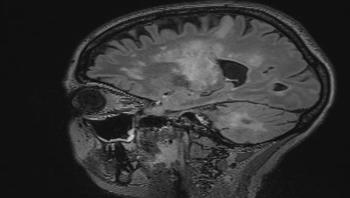
Researchers from the University of Zurich and the University Hospital Zurich reveal possible new treatment methods for a rare, usually fatal brain disease. Thanks to their discovery that specific antibodies play a key role in combating the viral infection, a vaccine against the disease progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy could now be developed.



This Pulse summarizes best practices associated with environmental cleaning and surface disinfection in the ambulatory-care environment. It highlights basic infection prevention recommendations for outpatient settings, and reaffirms Standard Precautions as the foundation for preventing transmission of infectious agents during patient care in all healthcare settings.

The implantation of medical devices is not without risks. Bacterial or fungal infections can occur and the body's strong immune response may lead to the rejection of the implant. Researchers at Inserm/Strasbourg University have succeeded in creating a biofilm with antimicrobial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties. It may be used to cover titanium implants such as orthopedic prostheses or pacemakers to prevent or control post-operative infections. Other frequently used medical devices that cause numerous infectious problems, such as catheters, may also benefit. These results are published in the journal Advanced Healthcare Materials.









The World Health Organization (WHO) is helping Sierra Leone to mobilize all its experience and partners to ensure that any new cases of Ebola are investigated and transmission of the disease stopped as rapidly as possible. Sad news that a 16-year-old girl had died from Ebola in Bombali district, a part of the country that had a large outbreak five months ago, sparked an immediate inter-agency rapid response. Partners sent people with the skills and equipment needed to stop further infection in Bombali.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), multiple states and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) continue to investigate a multi-state outbreak of Salmonella Poona infections. Currently, 558 people infected with the outbreak strains of Salmonella Poona have been reported from 33 states, an increase of 140 cases since the last update on Sept. 15; 112 ill people have been hospitalized, and three deaths have been reported from Arizona, California and Texas; 52 percent of ill people are children younger than 18 years.
