
News






This digital issue explores the challenges associated with proper cleaning and disinfection in the sterile processing department (SPD).
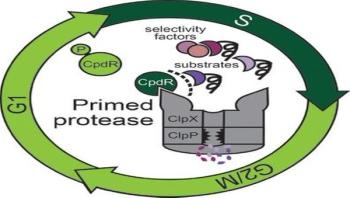
As part of their long-term investigation of regulatory factors in the bacterial cell cycle, molecular biologists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst now report finding a surprising new role for one factor, CpdR, an adaptor that helps to regulate selective protein destruction, the main control mechanism of cell cycle progression in bacteria, at specific times.

A Purdue University-led team of researchers studying the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), have found molecules that shut down the activity of an essential enzyme in the virus and could lead the way to better treatments for those infected.


The family of Bernard Lansana Soumah never expected to experience Ebola. When Bernard’s wife, Macire, became infected, they realized Ebola was real. Today, Bernard and Macire are among the lucky ones and they are vigilant in watching for signs of infection among those in their community while also providing a message of survival and hope.







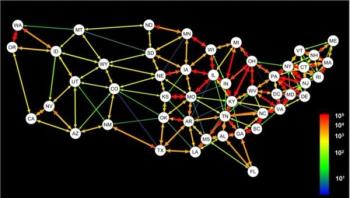
To predict how a seasonal influenza epidemic will spread across the United States, one should focus more on the mobility of people than on their geographic proximity, a new study suggests. PLOS Pathogens published the analysis of transportation data and flu cases conducted by Emory University biologists. Their results mark the first time genetic patterns for the spread of flu have been detected at the scale of the continental United States.

Infection prevention is a constantly changing field. Tremendous challenges face the infection preventionist (IP), including new emerging and re-emerging diseases, antibiotic resistant organisms, serious; often life-threatening diseases such as C. difficile, public reporting of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) policies to limit payment for hospital-acquired conditions and complications.

Infection Control Today invited manufacturers of personal protective equipment (PPE) and antimicrobial textiles to share their perspectives on key issues relating to pandemic preparedness as well as proper donning and doffing techniques.
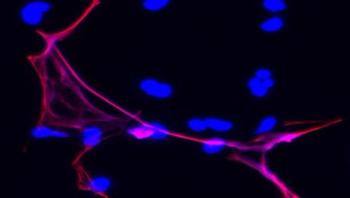
One of the body's tools for fighting off infection in a wound may actually slow down the healing process, according to new research by a team of Harvard University, Boston Children's Hospital, and Penn State University scientists. In a study published online in Nature Medicine on June 15, 2015, the researchers show that they can speed up wound healing in diabetic mice by preventing immune cells called neutrophils from producing structures called NETs (neutrophil extracellular traps) that trap and kill bacteria.






More than a month has passed since Ebola transmission ceased in Liberia. This hard-fought achievement is still being celebrated across the country, where nearly 11,000 people became infected with the virus and 4,800 died. Liberia is still urging communities not to let their guard down until Ebola is gone from the region. They are working closely with WHO and other partners to keep Ebola from reemerging.