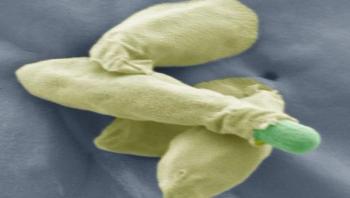
Tokay geckos harbor bacteria that are resistant to a number of antibiotics, making them a health concern for pet owners, according to a study by University of Georgia researchers. Tokay geckos, a type of gecko known for the "to-kay" sound it makes, are caught in the wild and often imported into the pet trade in the U.S.