News

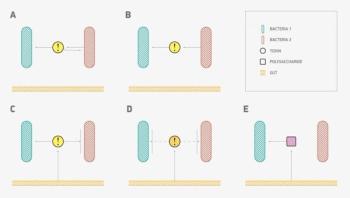
Researchers from the Scientific Research Institute of Physical-Chemical Medicine, MIPT, the company M&S Decisions and the research department of Yandex have built a computer model of the interaction between different bacteria, and between bacteria and the gut wall. This has led them to explain how antibiotic-resistant microbes develop and spread; details of the study have been published in the journal PLOS ONE.


An effective vaccine against the virus that causes genital herpes has evaded researchers for decades. But now, researchers from the University of Illinois at Chicago working with scientists from Germany have shown that zinc-oxide nanoparticles shaped like jacks can prevent the virus from entering cells, and help natural immunity to develop.

Fungal infections are a serious problem in modern healthcare. A critical factor in their successful treatment is time: the faster they are detected, the more effectively dangerous infections can be prevented. At the Institute of Physical Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Warsaw a chemical sensor has been devised enabling the detection time of fungi to be shortened from the current couple of days to just a few minutes.



When human cells are exposed to titanium dioxide without the presence of UV light from the sun, the risk for bacterial infection more than doubles. This finding by a Stony Brook University-led research team, published early online in the Journal of Nanobiotechnology, raises concerns about exposure to titanium dioxide, a nanoparticle commonly used in millions of products worldwide ranging from cosmetics to toothpaste, gum, food coloring and medicines.






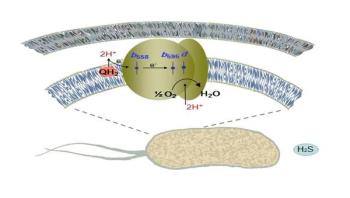
An international team of including the Lomonosov Moscow State University researchers discovered which enzyme enables Escherichia coli bacterium (E. coli) to breathe. The study is published in the Scientific Reports.