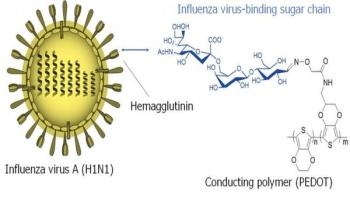
Researchers have developed a new, rapid biosensor for the early detection of even tiny concentrations of the human influenza A (H1N1) virus. Such early-stage diagnosis is crucial for averting a potential pandemic outbreak, as antiviral medication must be administered in a timely fashion. Conventional tests for detecting the flu virus are often slow and expensive, and can miss early viral infections. In contrast, the new biosensor measures tiny changes in voltage in an electrically conductive polymer to quickly detect virus concentrations almost 100 times smaller than the limit of currently available kits. The work was done at the Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU), in a collaboration between the Institute of Biomaterials and Bioengineering and the Department of Molecular Virology.