
News




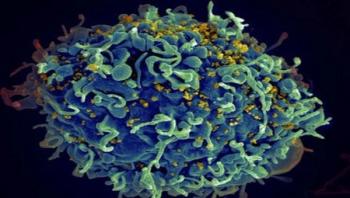
Vaccines are usually medicine’s best defense against the world’s deadliest microbes. However, HIV is so mutable that it has so far effectively evaded both the human immune system and scientists’ attempts to make an effective vaccine to protect against it. Now, researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania have figured out how to make a much-improved research tool that they hope will open the door to new and better HIV vaccine designs. George M. Shaw, MD, PhD, a professor of Hematology/Oncology and Microbiology, and Hui Li, MD, a research assistant professor of Hematology/Oncology, published their results in the early online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.

Emerging evidence suggests a broader range of possible complications for babies born to women affected with Zika virus. These could go beyond microcephaly to effects on other brain abnormalities. The World Health Organization (WHO) is coordinating efforts to understand the broader range of complications that define congenital Zika virus syndrome and invites partners to join in this effort.
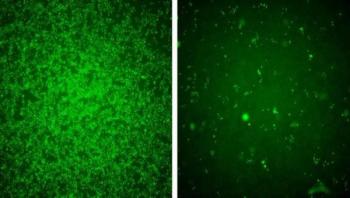
Eight weeks after receiving their first samples of Zika virus, scientists at the University of Massachusetts Medical School (UMMS) have shown that a very small protein we all have in our bodies, interferon-induced protein 3 (IFITM3), can dramatically reduce the ability of Zika virus to infect human and mouse cells. In some cases, IFITM3 can also prevent Zika virus from killing our cells. The findings, by senior author Abraham Brass, MD, PhD, assistant professor of microbiology & physiological systems, suggest that boosting the actions of IFITM3 may be useful for inhibiting Zika virus and other emerging viral infections. The study appears in the journal Cell Reports.



Antimicrobial resistance (AR), the phenomenon whereby microbes gradually develop resistance to agents used to eradicate them, is rapidly becoming a severe and urgent threat to global public health. Thanks to AR, a wide range of infections – even those once considered routine – are developing ultimately life-threatening potential by becoming increasingly difficult to treat until eventually untreatable, and consequently rates of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), morbidity and mortality are increasing. Unfortunately, as AR rises and our arsenal of antimicrobial weaponry falls, some of the greatest achievements of modern medicine – such as organ transplantation and other complex surgeries, as well as cancer chemotherapy – may be invalidated.

Infection prevention continues to be an issue that is top of mind for GI professionals. When thinking of gastroenterology infection prevention, it traditionally has been in terms of reprocessing endoscopes and post-procedure patient phone call to assess for infections. Infection prevention for GI encompasses so much more than those two tasks - it includes correct use of personal protective equipment (PPE), personal hygiene, engineering controls of the physical environment, cleaning and disinfection of surfaces, training, continuing education, written operating procedures, and of course documentation. Earlier this year, SGNA released practice documents focused on infection prevention. The new document, Standard of Infection Prevention in the Gastroenterology Setting, brings to light an important point that is often overlooked when we discuss infection prevention: Prevention for the whole team.



Serious health and safety concerns for healthcare, public safety and support service personnel arose after the 2014 Ebola virus disease that resulted in 11,000 deaths across multiple countries, with four confirmed cases in the United States. In the event of an Ebola or other infectious disease outbreak, the responsibility for patient transfer, assessment and testing falls on the local healthcare and public safety systems. Investigators at the University of Alabama at Birmingham recently received a grant to provide safety and health training to healthcare and public safety workers through the UAB Deep South Biosafety and Infectious Disease Response Training Consortium. Co-program directors, Lisa McCormick, DrPH, and Marjorie Lee White, MD, will develop and implement a training program to equip workers with the skills and knowledge needed to protect themselves and their communities from potential exposure to contaminated materials or infected individuals they may encounter.











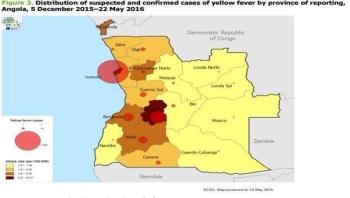
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) has updated its rapid risk assessment on the outbreak of yellow fever with the latest developments, more comprehensive information on the current situation in Angola, Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and Uganda and an extended threat assessment for the EU. Some of the data used in the assessment were collected during a mission to Angola in May 2016.
