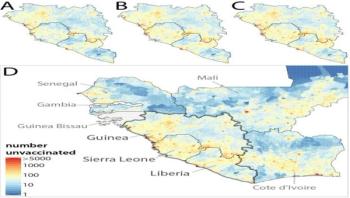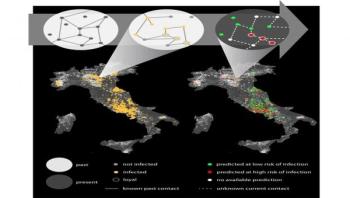
Research publishing this week in PLOS Computational Biology analyzes the livestock trade in Italy and sexual encounters in a Brazilian prostitution service to find a correlation between loyalty and infection risk. The French team at Inserm, in collaboration with ISI Foundation and Istituto Zooprofilattico Abruzzo-Molise in Italy, has shown that it is possible to use past contact data to predict the risk of infection in emerging outbreaks.