
News



Water is essential for life, and we are fortunate to have safe, affordable drinking water from municipal sources. Though water meets drinking standards when it enters a building, the complexity of healthcare building water systems can create conditions that allow growth of microorganisms, including waterborne pathogens that have been linked to healthcare-associated infections (HAIs).

Quality improvement (QI) in healthcare is a noble initiative but an increasing number of clinicians and administrators are wondering if such efforts are paying off in terms of better outcomes and whether or not they can be sustained long-term. Some studies indicate an ongoing disconnect between QI program goals and actual results. As Schouten, et al. (2008) remark, "The multi-institutional, quality improvement collaborative is widely accepted as a strategy in healthcare. Its widespread acceptance and use are not, however, based on a systematic assessment of effectiveness."



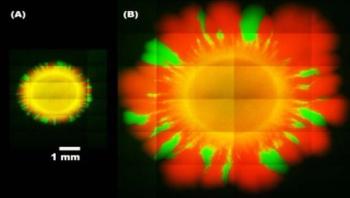
The ability of pathogenic bacteria to evolve resistance to antibiotic drugs poses a growing threat to human health worldwide. And scientists have now discovered that some of our microscopic enemies may be even craftier than we suspected, using hidden genetic changes to promote rapid evolution under stress and developing antibiotic resistance in more ways than previously thought. The results appear in a new paper in the journal Biomicrofluidics, from AIP Publishing.





Today on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)’s Safe Healthcare Blog, Dr. Steven Simpson, Sepsis Alliance board of directors member, shares his hypothesis on why many of his peers say they don’t see much sepsis in their practices and don’t know how to recognize symptoms of the condition until it gets to the point of septic shock.






CNN.com is reporting that the Office of the Inspector General says that the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) is "ill-prepared" for an outbreak such as the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic or a global Ebola outbreak.







