
Environmental Services
Latest News







The resurgence of bed bugs over the last decade has caused problems in major U.S. cities where they infest homes, apartments, hotels, shelters and even places of work. The small, blood-feeding insects are not known to transmit diseases, but they can cause severe reactions in people who are allergic to them. Bed bugs usually go unnoticed until their numbers increase significantly, and getting rid of them can be costly.









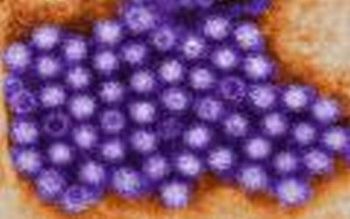
Healthcare facilities that experience outbreaks of norovirus are challenged with disinfection methods, case histories and control measures. Because the norovirus is highly contagious and lives in the inanimate environment, isolation and cleaning practices must be vigilant.



Infection Control Today asked members of industry to share their best advice to infection preventionists and purchasing managers when evaluating microfiber and healthcare textiles relating to infection prevention best practices.




Local activists continue to voice their objections at area hospitals over the practice of trucking infectious medical waste through local communities to be treated at a remote facility. As Safe Hospitals Safe Communities spokesperson Debra Pelletier notes, "We are visiting area hospitals to raise awareness about the transportation of medical waste through local communities and ask for safer disposal of medical waste. Nearly 1,000 hospitals now use on-site sterilization technologies that prevent infectious medical waste from being trucked through our neighborhoods, thus stopping the spread of infectious pathogens and preventing possible accidents and spills."

