News




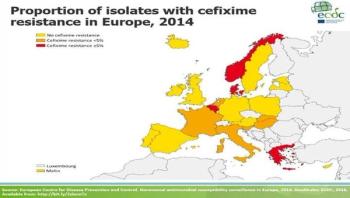
In 2014, the susceptibility of gonococci to two of the recommended antibiotics for gonorrhea treatment has shown signs of improvement, according to results from the European Gonococcal Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (Euro-GASP). At the same time, a significant increase in resistance to another antibiotic agent that is part of the suggested dual therapy of gonorrhea was observed.



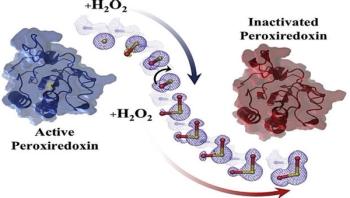
Researchers have made the first-ever detailed, atomic-level images of a peroxiredoxin, which has revealed a peculiar characteristic of this protein and might form the foundation for a new approach to antibiotics.

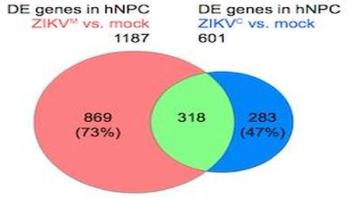
Scientists have revealed molecular differences between how the African and Asian strains of Zika virus infect neural progenitor cells. The results could provide insights into the Zika virus' recent emergence as a global health emergency, and also point to inhibitors of the protein p53 as potential leads for drugs that could protect brain cells from cell death.
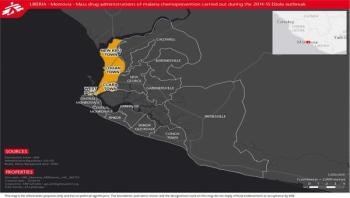
Mass drug administration may have reduced malarial incidence during the 2014 Ebola outbreak in Liberia, according to a study published August 31, 2016 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Anna Kuehne from Epicentre, France, and colleagues.




When looking at bacteria, you typically see also flagella: long hairs that protrudes from the bacteria's body. The key function of the flagella is movement - what scientists call "motility." The flagella give the bacteria the ability to swim in their environment by rotating like propellers. Bacteria can have a different number of flagella, and flagella are important because there is a clear correlation between motility and infection. Dr. Hideyuki Matsunami of the Trans-Membrane Trafficking Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST), together with a team of scientists, explored some aspects of the formation of flagella in research that may have implications for contrasting bacterial infections. They published their findings in Scientific Reports
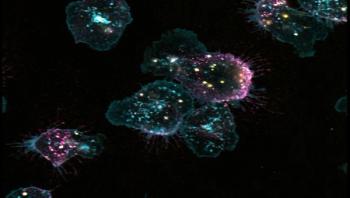
As an arm of the innate immune system, white blood cells called neutrophils form the first line of defense against invading pathogens. Neutrophils spend most of their lives racing through the bloodstream, patrolling for bacteria or other foreign particles. Once they arrive at tissues besieged by infectious agents, they halt on a dime and then blast through the vessel wall to reach the inflammatory attack site. They do this by activating integrins, a class of adhesion receptors that can switch on in less than a second.


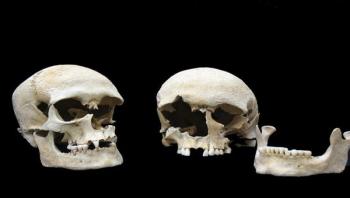
Before the infamous Black Death, the first great plague epidemic was the Justinian plague, which, over the course of two centuries, wiped out up to an estimated 50 million (15 percent) of the world's population throughout the Byzantine Empire----and may have helped speed the decline of the eastern Roman Empire. No one knows why it disappeared.

In a study of children with brain shunts at Children's of Alabama, a University of Alabama at Birmingham investigational biomarker outperformed the current "gold standard" test for detecting bacterial infections in the shunts.

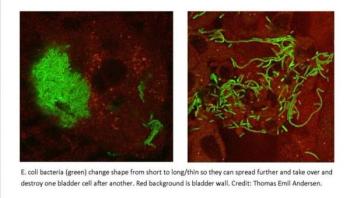
Every year, millions of people are treated for cystitis, but despite its prevalence, the disease is still a scientific mystery. Now a research team from University of Southern Denmark has succeeded in identifying how the bacteria responsible for the disease cause the disease to develop. This is a cause for optimism that more effective treatment methods can be developed.

As researchers gain increasing experience with UV-C light, they are reporting encouraging results related to efficacy against some of the most problematic pathogens in hospitals today.