
News









Q: Currently our process for hand-washed items is that once they are placed in the window one of my staff members wipes the item down with alcohol and then will blow it out (if necessary) place it in the dryer or prepare for sterilization. We do not wear gloves during this process. I have reached out to other facilities and they do not either. I have a new employee who is uncomfortable with wiping off items that come through the window without wearing gloves. What is the best practice?




Too much dietary zinc increases susceptibility to infection by Clostridium difficile (C. diff) according to research findings reported Sept. 26 in Nature Medicine, call into question the consumption of dietary supplements and cold therapies containing high concentrations of zinc.




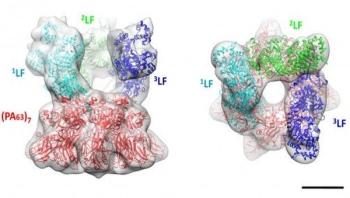
Researchers have built a three-dimensional map of the anthrax toxin that may explain how it efficiently transfers its lethal components into the cytoplasm of infected cells. The study, “Structure of anthrax lethal toxin prepore complex suggests a pathway for efficient cell entry,” which will be published online September 26 ahead of print in The Journal of General Physiology, suggests that the bacterial protein acts as a “conveyer belt” that allows toxic enzymes to continuously stream across cell membranes.










