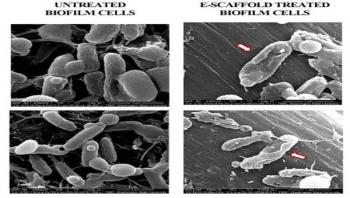
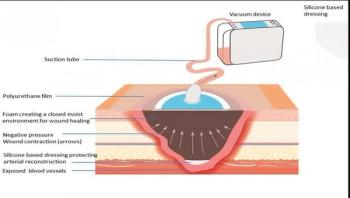
When it comes to preventing infection in the perioperative environment, infection preventionists and perioperative nurses are strong allies. We collaborate to share our unique perspectives on patient safety and uncover little known dangers or risks that put our patients at increased risk for exposure to infectious disease. However, there is a dangerous vehicle for infection transmission in the OR that is lurking right under our noses, literally-that danger is surgical smoke.