
News












Outsourcing is a strategy that healthcare institutions employ to help curb the escalating costs of providing services. In healthcare, as in other industries, outsourcing entails hiring an external contractor that assumes responsibility for managing a service line. Because the contractor specializes in providing a specific service and can achieve economies of scale, the entity can provide a service more efficiently and less expensively than the healthcare organization. In the case of healthcare laundry outsourcing, moving this service that is peripheral to the institutions primary operation of providing clinical services may also enable administrators and staff to concentrate more efficiently on their core business.
















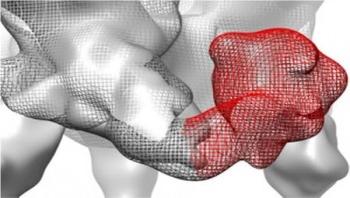
UC Davis researchers are getting a new look at the workings of HIV and other viruses thanks to new techniques in electron microscopy developed on campus. The envelope (or Env) protein of HIV is a key target for vaccine makers: it is a key component in RV144, an experimental vaccine that is so far the only candidate to show promise in clinical trials. Also called gp120, the Env protein associates with another protein called gp41 and three gp120/gp41 units associate to form the final trimeric structure. The gp120 trimer is the machine that allows HIV to enter and attack host cells.
