
News






A University of Saskatchewan (U of S) research team has discovered a way to prevent bacteria from developing resistance to antibiotics, potentially helping to blunt the edge of a looming threat to public health around the world.






Rapid testing for the Zika virus is a critical need in the recent Ebola-affected countries of Liberia, Sierra Leone and Guinea, says a Georgetown University professor, because of the recent Zika outbreak on nearby Cape Verde and the similarity in symptoms between Zika and early Ebola.
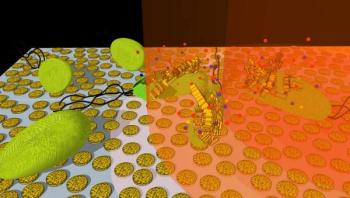
Researchers have developed a new technique for killing bacteria in seconds using highly porous gold nanodisks and light, according to a study published today in Optical Materials Express, a journal published by The Optical Society. The method could one day help hospitals treat some common infections without using antibiotics, which could help reduce the risk of spreading antibiotic resistance.


Health authorities from Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone and representatives of partner organizations have expressed confidence in the capacity of the three Ebola-impacted countries to effectively manage residual risks of new Ebola infections-pointing to the rapid government-led containment of recent flare-ups of the disease.




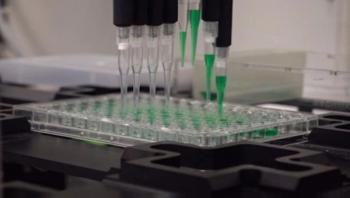
The antimicrobial arsenal that we count on to save millions of lives each year is alarmingly thin--and these microbes are rapidly evolving resistance to our weapons. But help may be on the way: In a study posted in the AMB Express, researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) show that automated techniques commonly used to screen new drugs for mammalian cell toxicity could also dramatically speed up the challenging task of antimicrobial discovery.



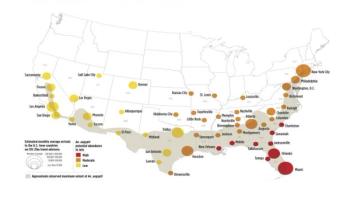
Key factors that can combine to produce a Zika virus outbreak are expected to be present in a number of U.S. cities during peak summer months, new research shows. The Aedes aegypti mosquito, which is spreading the virus in much of Latin America and the Caribbean, will likely be increasingly abundant across much of the southern and eastern United States as the weather warms, according to a new study led by mosquito and disease experts at the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR).




There is only one class of antiviral medicines against herpesviruses - a family of viruses that cause mononucleosis, herpes, and shingles, among other illnesses - meaning options for treating these infections are limited. If viruses become resistant to these frontline treatments, a growing problem particularly in clinical settings, there are no alternative drugs to serve as backup.
