News
















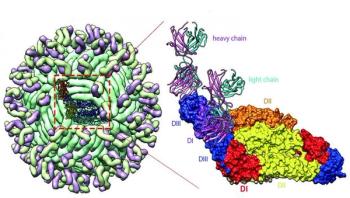
Researchers have identified neutralizing antibodies against Zika virus from an infected patient that fully protected mice from infection, adding to the current arsenal of antibodies in development for much needed antiviral therapies and vaccines. Unlike other human antibodies under investigation that recognize both Zika and the closely related dengue virus, the antibodies used in this study exclusively target Zika, demonstrating a high specificity that could be important in avoiding potential side effects - such as enhanced dengue infection in regions where both viruses are endemic.
A key skin protein previously overlooked in studies of staph infection has the ability to quell antibiotic-resistant staph- and strep-based skin infections, according to a study in the Nov. 18, 2016 issue of Science Immunology.

A Rift Valley fever outbreak was recently reported at the border between Niger and Mali in West Africa. So far, 64 human cases including 23 deaths have been confirmed in Niger, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Umeå University infectious disease epidemiologist Osama Ahmed Hassan recently joined an international expert fact-finding mission to Mali as a consultant with the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO/UN).

Healthcare provider burnout is known to have a relationship with both quality of care and patient safety. Psychologists from the School of Science at Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis conducted the first study to systematically, quantitatively analyze the links between healthcare provider burnout and healthcare quality and safety across medical disciplines.

OpenNotes evidence has shown that transparent medical records can increase patient engagement - patients who read the clinical notes written by their doctors report feeling more in control of their care and being better able to adhere to the treatment plan. Now new research from OpenNotes investigators at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) suggests that offering patients a mechanism to provide feedback about their notes further enhances engagement and can improve patient safety. The study results appear online today in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) Quality and Safety.

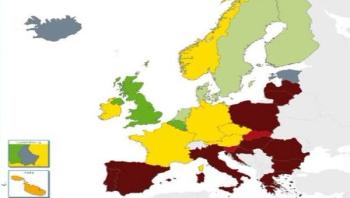
Acinetobacter baumannii is the cause of difficult-to-treat infections in healthcare settings in Europe due to its increasing resistance to antimicrobial agents, in particular the carbapenems. Outbreaks of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii in healthcare facilities have been reported in Europe and worldwide.