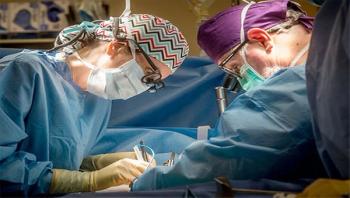
Sometime in the next few days or weeks - whenever he can adequately gather his thoughts - a Mississippi man plans to sit down and write a very important letter to a family he has never met, but whose legacy he will carry with him for the rest of his life. The man, who is HIV-positive, is in his 30s and wishes to remain anonymous. He recently became the eighth patient in the United States to receive a transplant from an HIV-positive deceased donor. The HIV-positive to HIV-positive transplant happened at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. UAB Hospital is the first in the Deep South to achieve an HIV-positive to HIV-positive transplant, and only the fourth hospital in the country to do so.