News


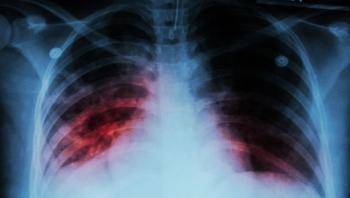
New genetic research from an international team including McMaster University, University of Helsinki, Vilnius University and the University of Sydney, suggests that smallpox, a pathogen that caused millions of deaths worldwide, may not be an ancient disease but a much more modern killer that went on to become the first human disease eradicated by vaccination.
Gautam Dantas remembers the day in 10th grade when he first wanted to be a scientist. It was the day he had a new biology teacher, a visiting researcher from the U.S. The teacher passionately described his own biochemical studies of how organisms live together in communities. By the end of the class, Dantas had resolved to earn a PhD in biochemistry. He ended up doing much more-gaining expertise in computational biology, protein design and synthetic biology. He now combines his skills and knowledge in multifaceted research that spans four departments at the Washington University in St. Louis. His goal: to better understand and help combat a vital public health threat-drug-resistant bacteria.


Bacterial resistance does not come just through adaptation to antibiotics, sometimes the bacteria simply go to sleep. An international team of researchers is looking at compounds that attack bacteria's ability to go dormant and have found the first oxygen-sensitive toxin antitoxin system.

Many infectious pathogens are difficult to treat because they develop into biofilms, layers of metabolically active but slowly growing bacteria embedded in a protective layer of slime, which are inherently more resistant to antibiotics. Now, a group of researchers at Caltech and the University of Oxford have made progress in the fight against biofilms. Led by Dianne Newman, the Gordon M. Binder/Amgen Professor of Biology and Geobiology, the group identified a protein that degrades and inhibits biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the primary pathogen in cystic fibrosis (CF) infections.



Every 18 seconds someone dies from tuberculosis (TB). It is the world's most deadly infectious disease. Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative agent of TB, has infected more than one-third of the entire human population with an annual death toll of approximately 1.5 million people. For the first time, an international team of scientists from Monash University and Harvard University have seen how, at a molecular level, the human immune system recognizes TB infected cells and initiates an immune response. Their findings, published in Nature Communications, are the first step toward developing new diagnostic tools and novel immunotherapies.








Australian researchers have found a new way to make one of the most common medical procedures in the world - placing drips or intravenous (IV) lines - safer, less painful and potentially more cost effective. The researchers, who were funded by the Emergency Medicine Foundation of Australia (EMF), found that using medical skin glue to hold hospital drips in place significantly reduced the need to replace them due to infection, pain, blockage or falling out.




An analysis of 2,000-year-old human remains from several regions across the Italian peninsula has confirmed the presence of malaria during the Roman Empire, addressing a longstanding debate about its pervasiveness in this ancient civilization. The answer is in mitochondrial genomic evidence of malaria, coaxed from the teeth of bodies buried in three Italian cemeteries, dating back to the Imperial period of the first to third centuries Common Era.
Part of the reason tuberculosis-causing bacteria are so good at colonizing the human body is that they have defenses against the body's immune system. A research team led by a Brown University chemist has developed a new compound that can take down one of those defenses in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The researchers are hopeful that the compound could be part of a new drug strategy for treating tuberculosis.
Syphilis has plagued humankind for over 500 years. After the first reported outbreaks struck Europe in 1495, the disease spread rapidly to other continents and swelled to a global pandemic. When treatment with the antibiotic penicillin became available in the mid-twentieth century, infection rates started to decrease dramatically. Strikingly, however, infection with the bacteria Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum (TPA) has been re-emerging globally in the last few decades; more than 10 million cases are reported annually. Yet the reason for the resurgence of this sexually transmitted infection remains poorly understood.

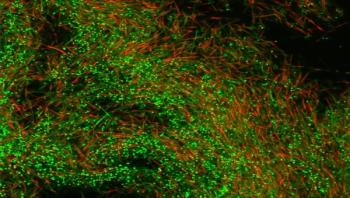
A world-first vaccine developed by Melbourne scientists, which could eliminate or at least reduce the need for surgery and antibiotics for severe gum disease, has been validated by research published this weekend in a leading international journal.
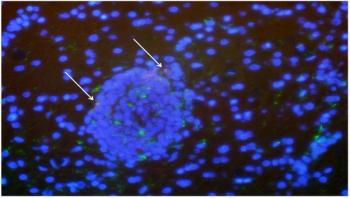
Combination drug treatments have become successful at long-term control of HIV infection, but the goal of totally wiping out the virus and curing patients has so far been stymied by HIV's ability to hide out in cells and become dormant for long periods of time. Now a new study on HIV's close cousin, simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), in macaques finds that a proposed curative strategy could backfire and make things worse if the virus is in fact lurking in the brain.
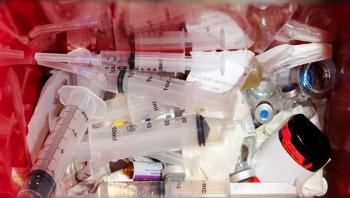
It has been 15 years since OSHA promulgated its 2001 updated Bloodborne Pathogens Standard to include additional requirements from the 2000 Needlestick Safety and Prevention Act. It is important to remind ourselves that this was the first and only Act passed unanimously by Congress into Law. In such heated political times with a new Presidency looming in January, we reflect to a time a decade and a half ago that we all agreed that preventing injuries from contaminated sharps was something that brought us all together in solidarity.